The Color Wheel
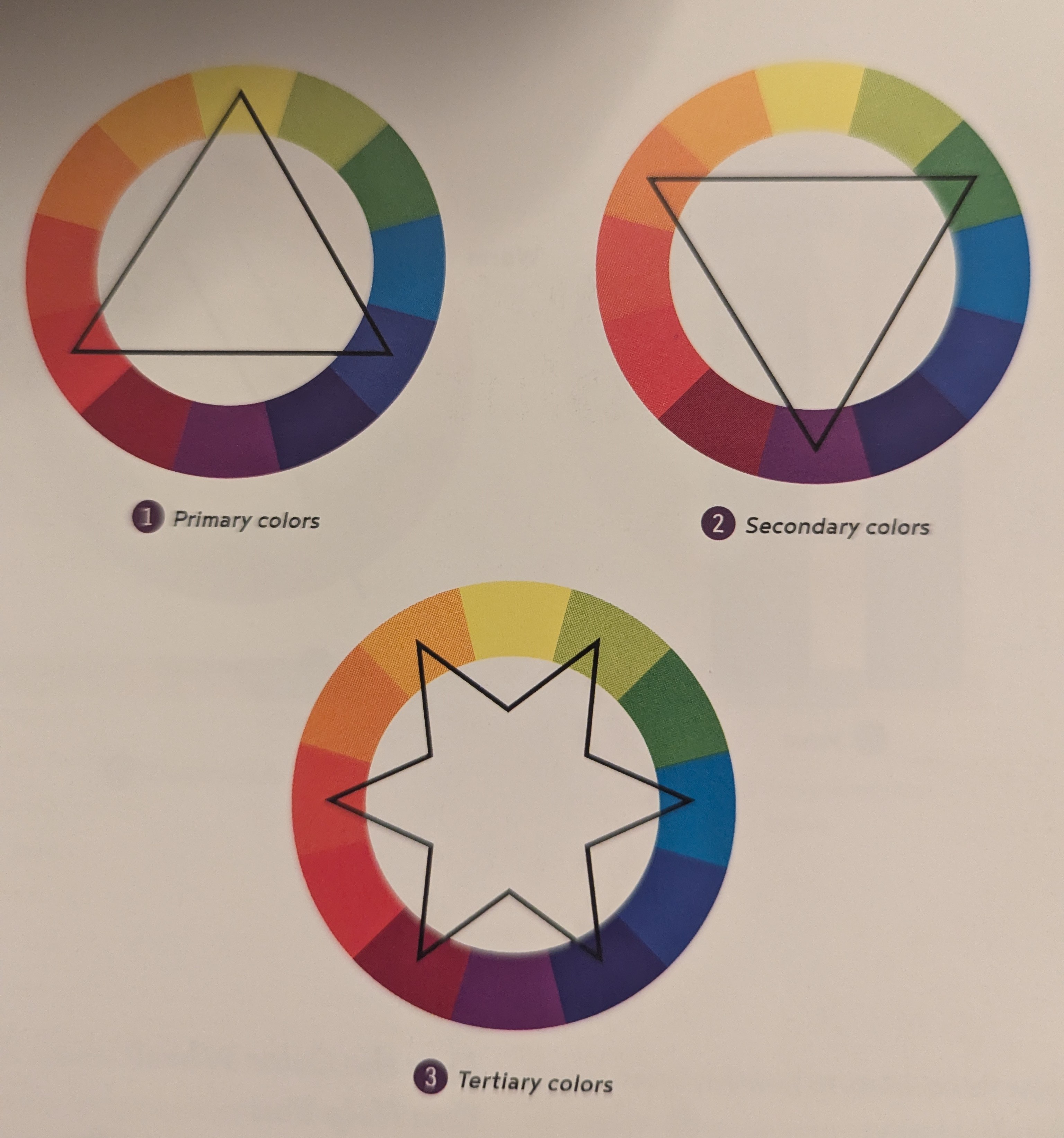
Hue - name of color group
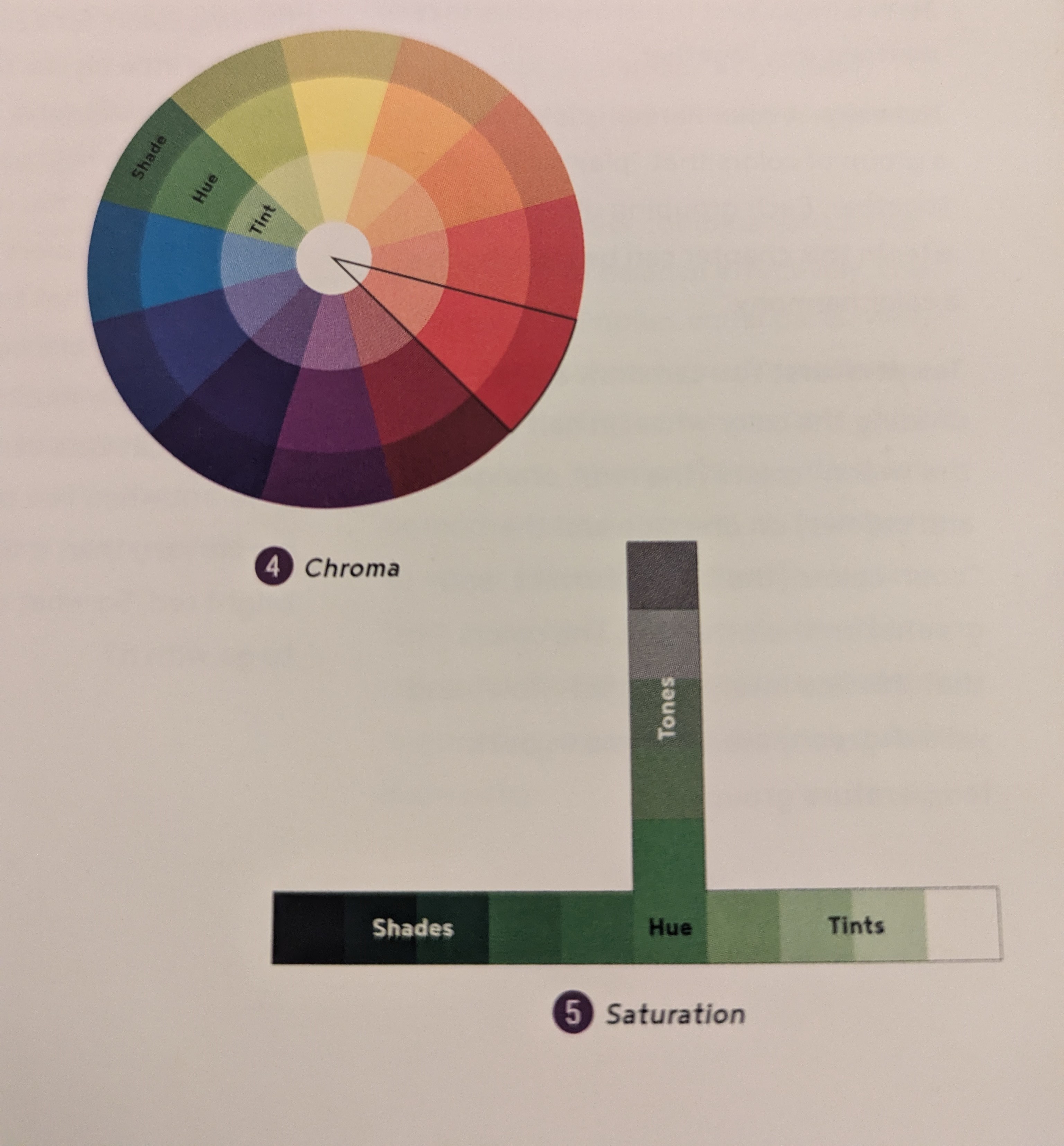
Chroma - all the different versions of any given hue
Saturation - how pure a color is
Tint - lightening a color/adding white
Shade - adding black
Tone - adding gray
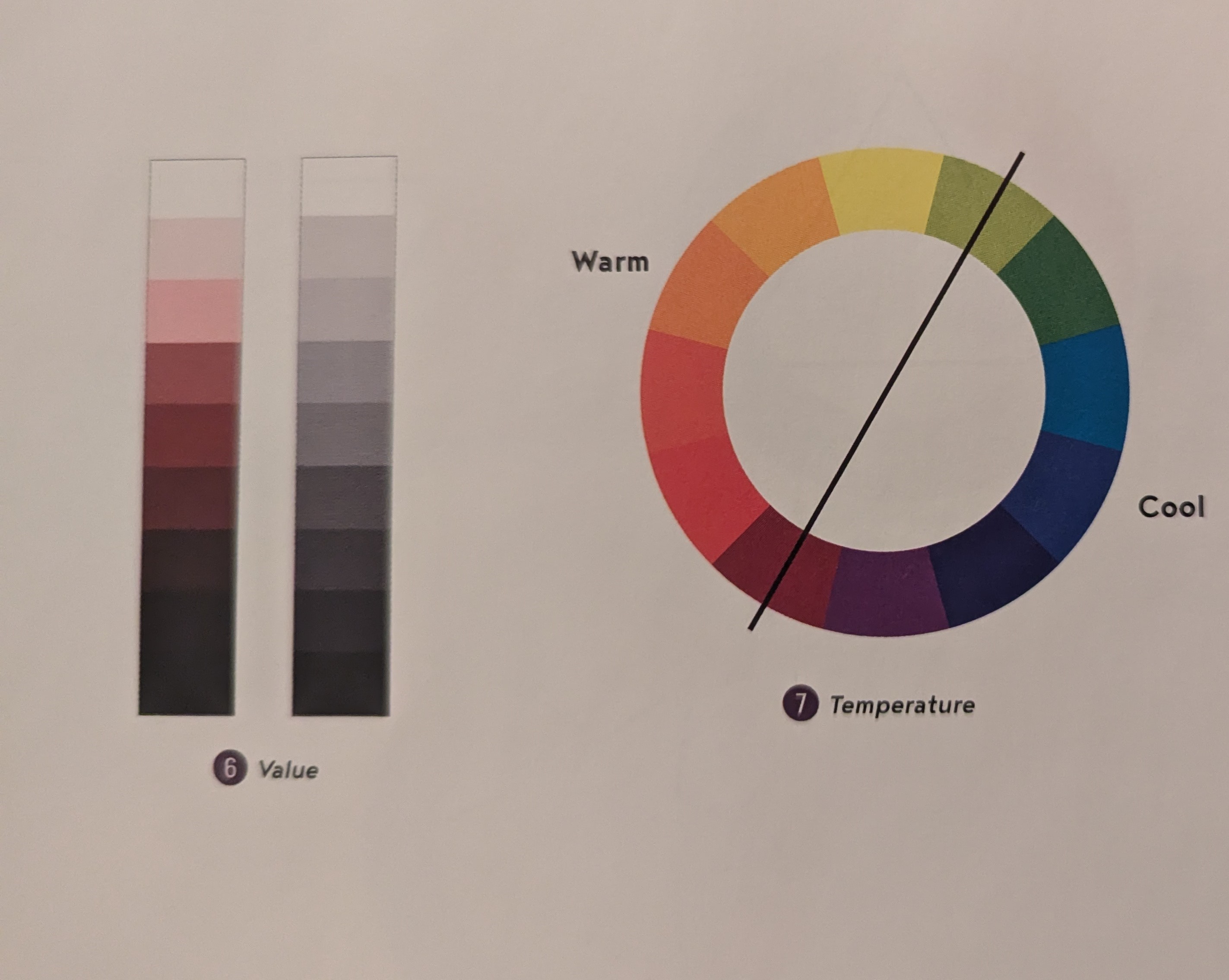
Value - how any given color would look on a grayscale
Temperature - Warm (red, orange, yellow undertones) & Cool (green, blue, purple undertones)
Color Schemes
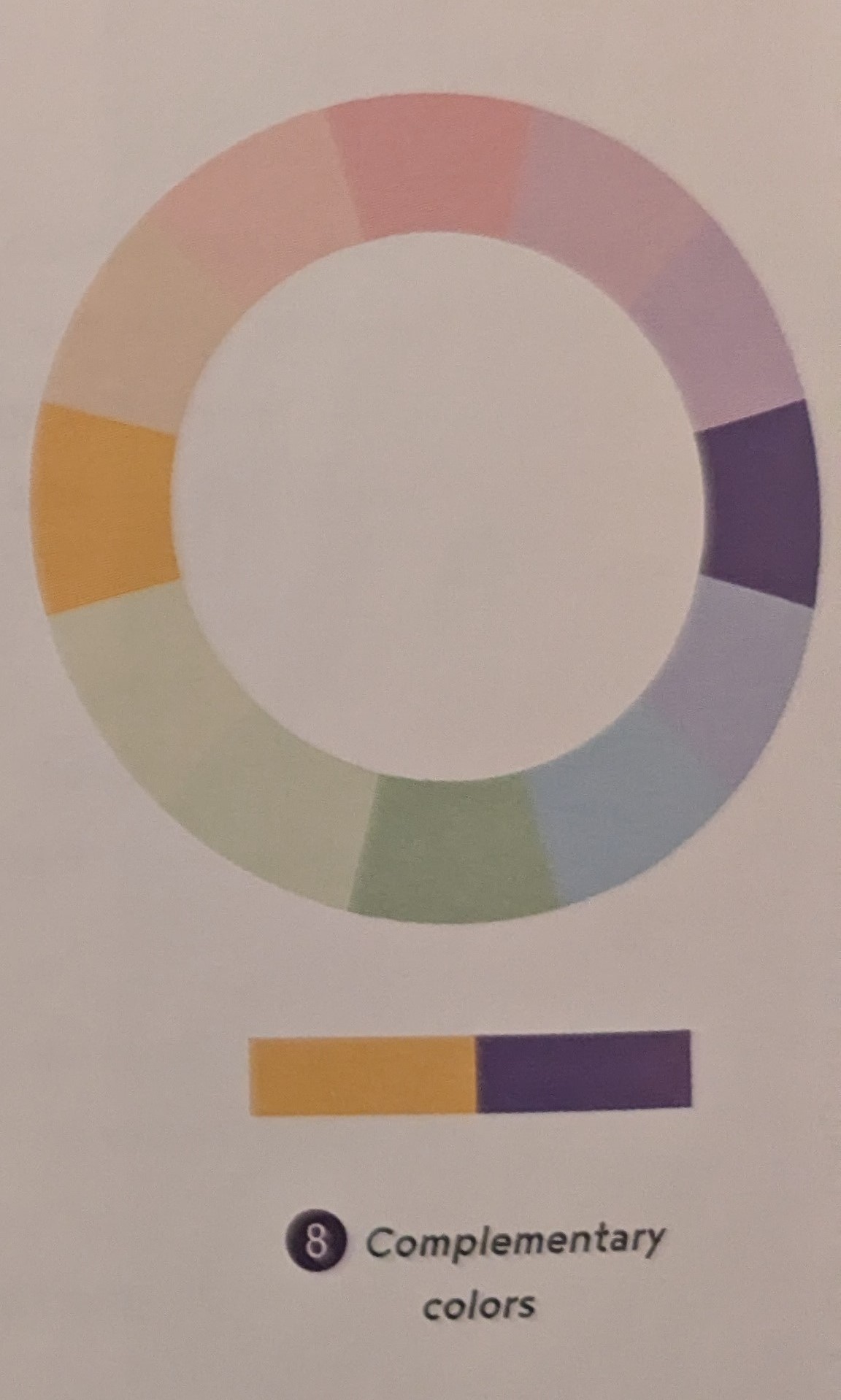

Complementary Colors - 2 colors that lie directly across from each other on the color wheel - High Contrast
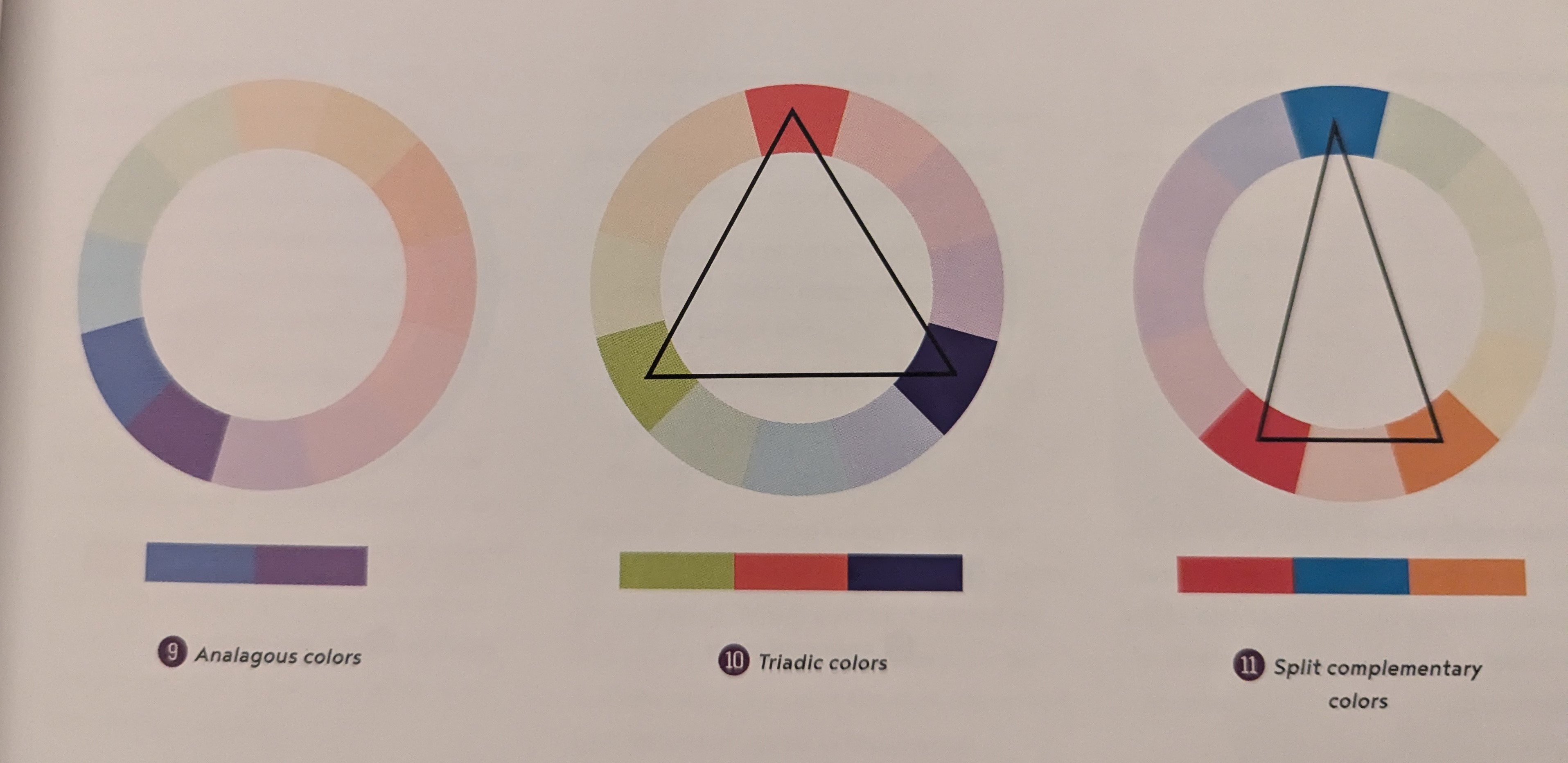
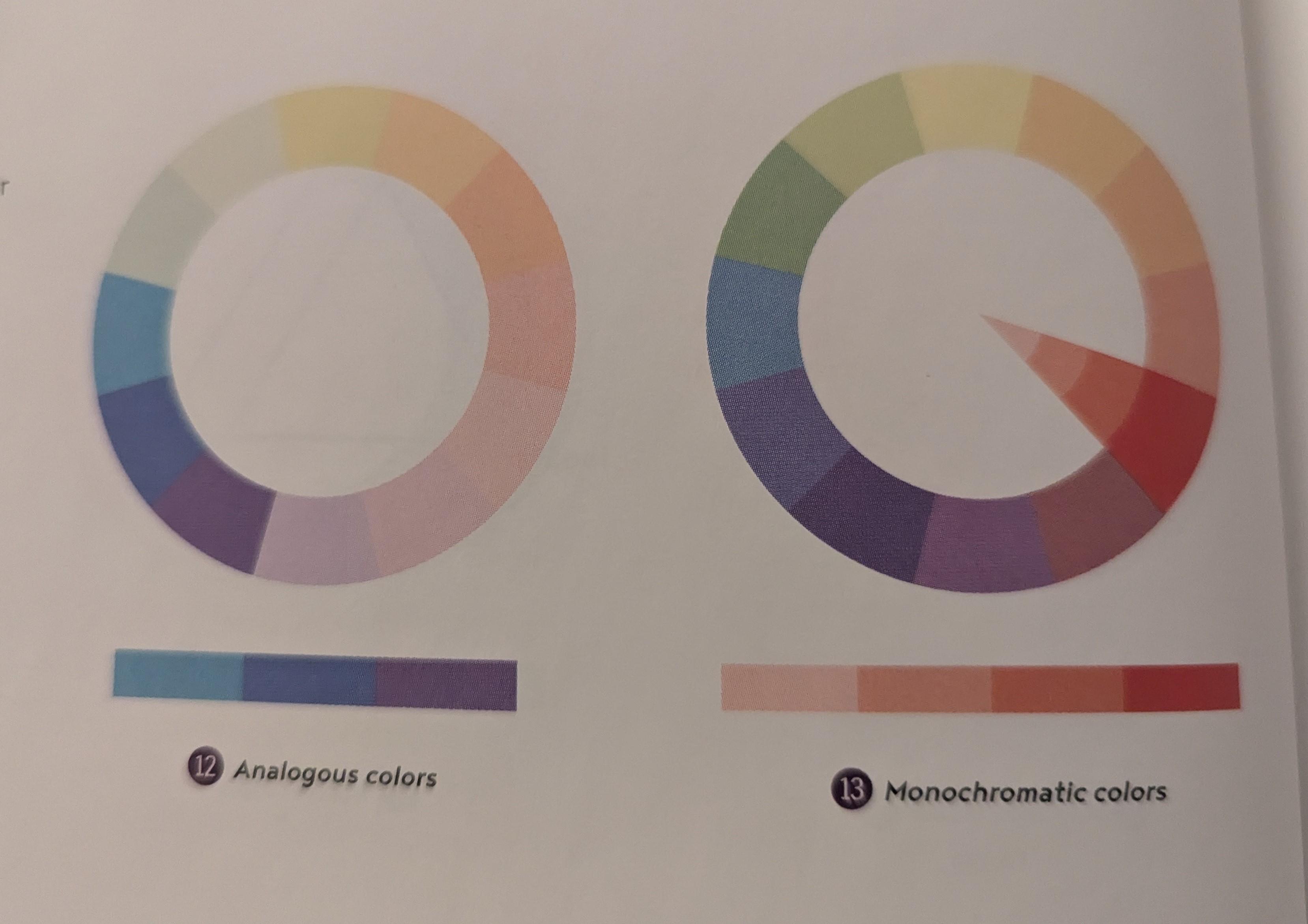
Analogous Colors - 2 colors that lie next to each other - Subtle, calm effect
Triadic Colors - 3 colors that form a perfect equilateral triangle on the color wheel - High contrast
Split Complementary Colors - 3 colors form an isosceles triangle - Not as dramatic, but strong visual contrast
Monochromatic Colors - 3 colors in 1 chroma, vary the tint/shade/tone of the color - Harmony always looks well-balanced & visually appealing; Lacks contrast in complementary color schemes
Double Complementary/ Tetradic Colors - 4 colors in a rectangular arrangement on the color wheel, pairing 2 complementary color pairs - Rich color scheme
Color Dominance
- Dominant - Warm colors, light values, light/bright tints
- Recessive - cool colors, dark values/tones/shades